Introduction
The Aschach Mesolithic archaeological site offers a fascinating window into prehistoric life, shedding light on how early humans adapted and thrived in their environment. Aschach, located in central Europe, is renowned for its Mesolithic discoveries, which bridge the gap between the Paleolithic and Neolithic periods. These findings reveal valuable information about the tools, lifestyle, and culture of Mesolithic communities.
In this article, we explore the key features of Aschach Mesolithic archaeology, including its historical significance, notable discoveries, and the methodologies used in uncovering its secrets. Whether you’re an archaeology enthusiast or a curious reader, this guide provides an in-depth look at one of Europe’s most intriguing prehistoric sites.
The Historical Significance of Aschach Mesolithic Archaeology
The Mesolithic period, often referred to as the Middle Stone Age, spans roughly 10,000 to 8,000 years ago. This era marks a critical transition as human societies evolved from hunter-gatherer lifestyles to more sedentary agricultural practices. Aschach stands out as a key site for understanding this period due to its well-preserved artifacts and evidence of early human innovation.
H2: A Unique Geographical Context
Situated near river valleys and forested areas, Aschach provided an ideal environment for Mesolithic communities. The abundant natural resources, including freshwater, wildlife, and plant life, supported sustainable living and enabled advancements in toolmaking and social organization.
H2: Contributions to Archaeological Understanding
Research at Aschach has contributed significantly to our knowledge of:
- Tool Development: Microliths, small stone tools found at the site, highlight the ingenuity of Mesolithic craftsmanship.
- Diet and Subsistence: Remains of animal bones, fish, and plant materials provide insight into the varied diet of Mesolithic people.
- Cultural Practices: Evidence of early art, burial practices, and potential ritual activities sheds light on the cultural complexity of these communities.
Notable Discoveries at Aschach
H2: Stone Tools and Microliths
One of the most remarkable findings at Aschach is the collection of microliths—small, intricately crafted stone tools that were likely used as components of composite tools such as spears or arrows. These tools demonstrate advanced techniques in flintknapping and the strategic use of available materials.
H2: Faunal and Botanical Remains
Archaeological excavations have unearthed a wealth of faunal remains, including deer, boar, and fish, as well as charred plant materials. These findings indicate a diet that was diverse and adapted to seasonal changes, showcasing the resourcefulness of Mesolithic communities.
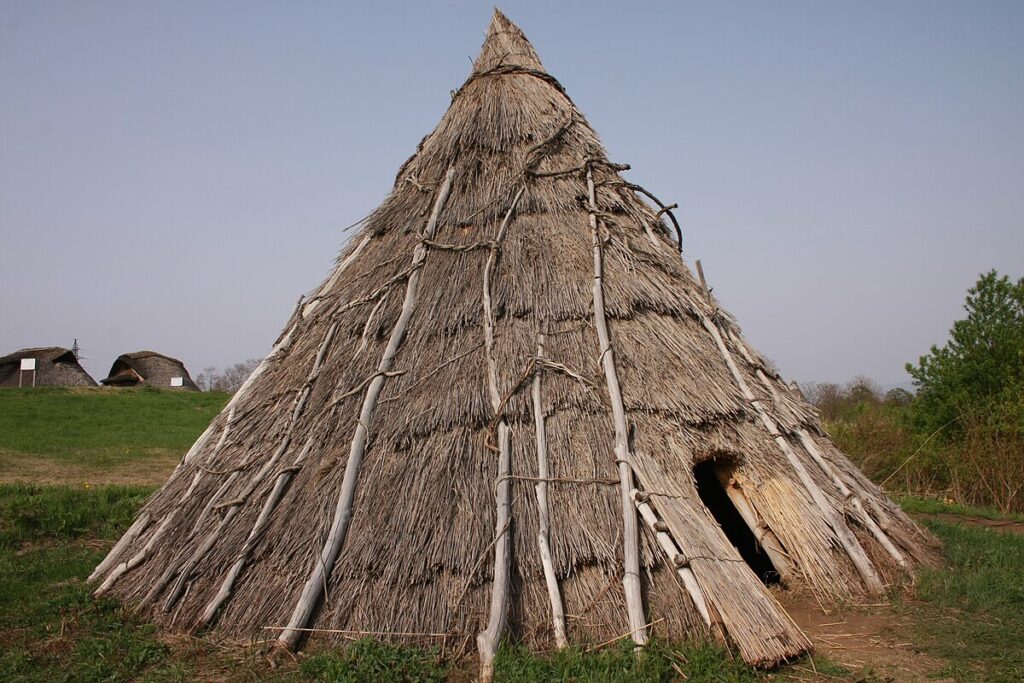
H2: Evidence of Habitation
Postholes and hearths found at the site suggest semi-permanent structures that may have been used seasonally. These findings provide clues about the social and domestic lives of Mesolithic people, including how they organized their living spaces.
Methodologies in Excavating Aschach
H2: Stratigraphic Analysis
Stratigraphy plays a crucial role in understanding the chronological sequence of the site. Layers of sediment are meticulously analyzed to determine the age of artifacts and the environmental conditions of the period.
H2: Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating of organic materials, such as charcoal and bone, has been instrumental in establishing an accurate timeline for the site’s occupation.
H2: Interdisciplinary Collaboration
The excavation and study of Aschach involve collaboration between archaeologists, paleoecologists, and anthropologists, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the site.
Preservation and Future Research
Efforts are underway to preserve the Aschach site and its artifacts for future generations. Advanced technologies, such as 3D scanning and GIS mapping, are being utilized to document and protect the site’s findings. Ongoing research continues to uncover new information, contributing to our understanding of Mesolithic life and its broader implications for human history.
Conclusion
The Aschach Mesolithic archaeological site serves as a vital link to our prehistoric past, offering invaluable insights into the lives of early humans. Through the study of tools, diet, and cultural practices, researchers have pieced together a vivid picture of Mesolithic communities and their adaptations. As excavation and preservation efforts continue, Aschach remains a cornerstone of archaeological exploration, inviting us to delve deeper into the mysteries of human history.