Introduction
In the field of directed energy systems, high-power lasers have become a crucial technology, especially in defense and industrial applications. However, efficiently combining multiple laser beams to achieve greater power while maintaining high beam quality has long been a technical challenge.
Patent US7970040B1 introduces an innovative apparatus for the incoherent combination of multiple high-power laser beams, simplifying beam alignment while preserving high-energy output. This technology represents a significant advancement, enabling robust, scalable laser systems for a variety of applications.
In this article, we will explore the details of US7970040B1, including how it works, its key features, and its potential applications across different industries.
Understanding Incoherent Laser Combining
What is Laser Combining?
Laser combining is a technique used to merge multiple laser beams into a single, more powerful beam. This process enhances the output power while maintaining beam quality and coherence. It is widely used in industrial, military, and scientific applications, including high-power laser systems, directed energy weapons, and fiber laser systems.
Types of Laser Combining
There are several methods to achieve laser beam combining:
- Spectral Beam Combining (SBC)
- Uses different wavelengths of laser light.
- Combines beams through a dispersive element (like a diffraction grating).
- Maintains high beam quality with minimal loss.
- Coherent Beam Combining (CBC)
- Uses phase control to align multiple laser beams.
- Requires precise phase-locking for constructive interference.
- Produces a single coherent beam with improved brightness.
- Polarization Beam Combining (PBC)
- Combines two beams with orthogonal polarization states.
- Uses a polarization beam splitter or waveplates.
- Effective but limited to doubling power.
- Spatial Beam Combining (SBC)
- Overlaps beams spatially using mirrors or lenses.
- Simple but may reduce beam quality.
Each method has its trade-offs in terms of efficiency, complexity, and beam quality. Spectral and coherent beam combining are the most advanced techniques, particularly in high-power laser applications.
Advantages of Incoherent Combining
- No need for phase alignment – Reduces system complexity and increases reliability.
- Easier scalability – Allows the addition of multiple laser sources without stringent coherence requirements.
- Better thermal management – Reduces beam distortions caused by thermal effects.
- Cost efficiency – Requires fewer high-precision optical components compared to coherent combining systems.
By leveraging these advantages, the technology described in US7970040B1 makes high-power laser systems more practical and effective.
Key Features of US7970040B1
1. Scalability and Modular Design
One of the key innovations of US7970040B1 is its ability to scale. The system allows multiple high-power lasers to be combined into a single output beam, making it adaptable to different energy requirements. Each laser module can deliver at least a kilowatt of power, and multiple modules can be integrated as needed.
This modular approach makes it ideal for:
- Military applications requiring adjustable power levels.
- Industrial settings where varying energy outputs are necessary.
- Research environments where scalable laser solutions are preferred.
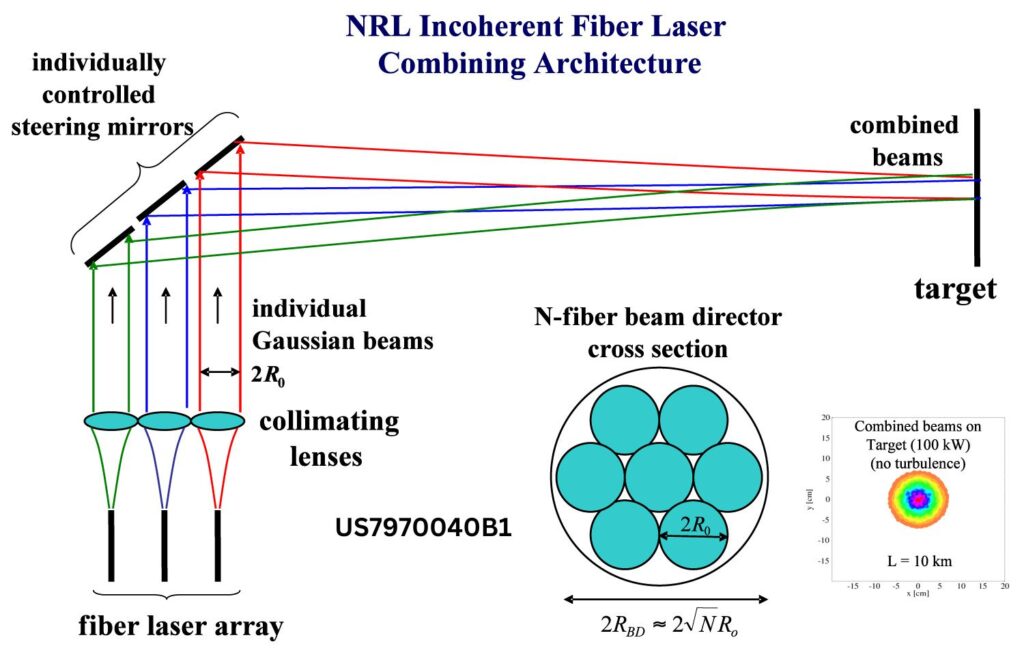
2. Advanced Beam Directing Mechanism
The patent describes a beam director that uses refractive optical elements and individually controllable steering mirrors. This setup allows precise focusing and directional control of the laser beams. The system employs:
- Adaptive optics to correct beam distortions.
- Tip-tilt compensation to ensure accurate targeting.
- Refractive optical elements for improved energy distribution.
These elements enhance the beam quality and ensure efficient energy delivery to the target.
3. Thermal Management System
One of the challenges in high-power laser systems is managing heat. Excessive heat can cause optical distortions, leading to reduced beam quality. US7970040B1 tackles this problem by incorporating an airflow generator that directs transverse airflow relative to the laser propagation path.
This airflow:
- Dissipates heat efficiently, reducing thermal lensing effects.
- Prevents optical degradation, maintaining beam consistency over extended operation periods.
- Improves system lifespan, making it more reliable for continuous use.
4. Operational Efficiency
- Simplified alignment procedures reduce setup time and maintenance requirements.
- Enhanced reliability due to fewer moving parts compared to coherent beam combining systems.
- Compact and lightweight design, making it suitable for mobile platforms and aerial applications.
Applications of US7970040B1
The technology behind US7970040B1 has potential applications across multiple industries, ranging from military defense to advanced manufacturing.
1. Defense and Directed Energy Weapons
The ability to combine multiple high-power lasers makes this system an excellent candidate for directed energy weaponry. Advantages include:
- Long-range targeting – The beam director ensures precise aiming at distant threats.
- Scalable power output – Adjusting laser modules allows for controlled energy delivery.
- Low collateral damage – Focused energy reduces unintended damage compared to traditional kinetic weapons.
The U.S. military and allied defense organizations could use this system in missile defense, anti-drone systems, and airborne laser platforms.
2. Industrial Manufacturing
The high-energy output of this system has significant implications for industrial applications:
- Laser cutting – High precision allows for detailed material processing.
- Welding and materials processing – Enhanced efficiency for joining metals and composites.
- Additive manufacturing (3D printing) – High-energy beams can improve the quality of laser sintering techniques.
3. Space and Aerospace Applications
Laser-based propulsion and communication systems stand to benefit from the innovations in US7970040B1. Potential applications include:
- Satellite-to-ground laser communication – High-power beams enable long-distance data transfer.
- Space debris removal – High-energy lasers can help disintegrate space debris.
- Propulsion technology – Focused laser beams may contribute to future propulsion systems for interplanetary travel.
4. Scientific Research and Medical Applications
In scientific and medical fields, the ability to control high-power lasers has applications in:
- Fusion energy research – High-energy lasers can be used to initiate nuclear fusion reactions.
- Medical laser treatments – High-power laser systems may enhance precision in surgical and dermatological procedures.
Comparison: Coherent vs. Incoherent Laser Combining
| Feature | Coherent Combining | Incoherent Combining (US7970040B1) |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Alignment | Required | Not Required |
| Complexity | High | Low |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
| Cost | Expensive | More Cost-Effective |
| Thermal Management | Challenging | Improved with Airflow System |
| Applications | Specialized | Versatile Across Multiple Fields |
The table above highlights why US7970040B1’s incoherent combining approach is more practical for large-scale, high-power applications.
Conclusion
Patent US7970040B1 represents a major innovation in high-power laser technology, offering a scalable, efficient, and cost-effective solution for combining multiple laser sources without requiring precise phase alignment. By addressing challenges in beam quality, thermal management, and operational efficiency, this invention paves the way for advancements in defense, industrial, aerospace, and scientific applications.
With its potential to revolutionize directed energy weapons, manufacturing, and space technologies, US7970040B1 is a significant step forward in laser engineering. As research continues, we can expect further refinements and new applications that harness the full potential of this innovative technology.